Definition, Explanation and Examples

In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment. When a company purchases goods or services from other companies on credit, a payable is recorded to show that the company promises to pay the other companies for their assets. Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets. If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity). Both sides of the accounting equation are always equal.
Accounting equation: More examples and explanation
If assets increase, either liabilities or owner’s equity must increase to balance out the equation. The opposite is true if liabilities or equity increase. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity). A company’s liabilities include every debt it has incurred. These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
Additional Resources
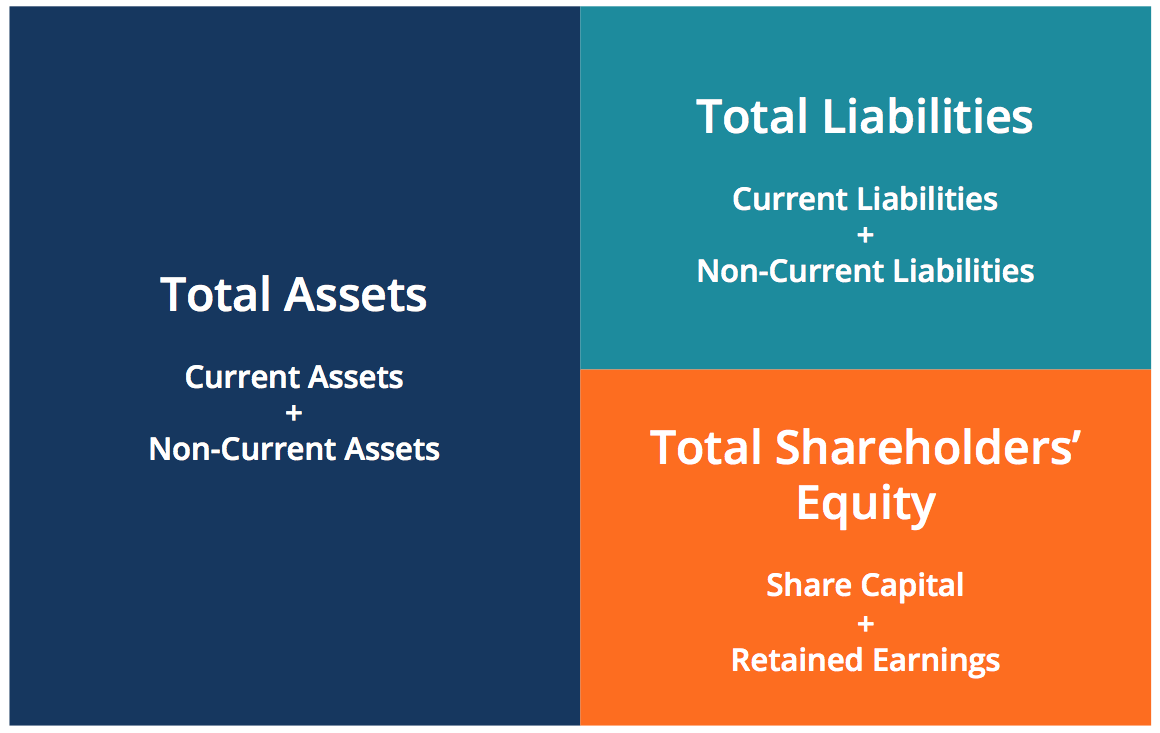
The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. For every transaction, both sides of this equation must have an equal net effect. Below are some examples of transactions and how they affect the accounting equation. At this point, the balance of total assets is $50,000. The combined balance of liabilities and capital is also at $50,000.
Understanding the Accounting Equation
If the net amount is a negative amount, it is referred to as a net loss. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry accounting system. Every financial transaction impacts at least two accounts, maintaining the balance. Anushka will record revenue (income) of $400 for the sale made.
The accounting equation will always balance because the dual aspect of accounting for income and expenses will result in equal increases or decreases to assets or liabilities. The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position and it reflects the accounting equation. The balance sheet reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s (or stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time. Like the accounting equation, it shows that a company’s total amount of assets equals the total amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity.
The accounting equation And how it stays in balance
- Accounts receivable list the amounts of money owed to the company by its customers for the sale of its products.
- The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner.
- Just like with our current assets and long term assets, we have the same threshold of 1 year.
- In order to help you advance your career, CFI has compiled many resources to assist you along the path.
Owners can increase their ownership share by contributing money to the company or decrease equity by withdrawing company funds. Likewise, revenues increase equity while expenses decrease equity. The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business. Like any brand new business, it has no assets, liabilities, or equity at the start, which means that its accounting equation will have zero on both sides. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity.
In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.
In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. Notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance. If the left recording inventory journal entries in your books examples side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation. The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.
コメントを残す