Accounting Equation Overview, Formula, and Examples

Assets will always equal liabilities and owner’s equity. As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets. So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved. Since the balance sheet is founded on the principles of the accounting equation, this equation can also be said to be responsible for estimating the net worth of an entire company.
Assets in Accounting: A Beginners’ Guide
Therefore cash (asset) will reduce by $60 to pay the interest (expense) of $60. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Equity represents the portion of company assets that shareholders or partners own.
Owners’ Equity
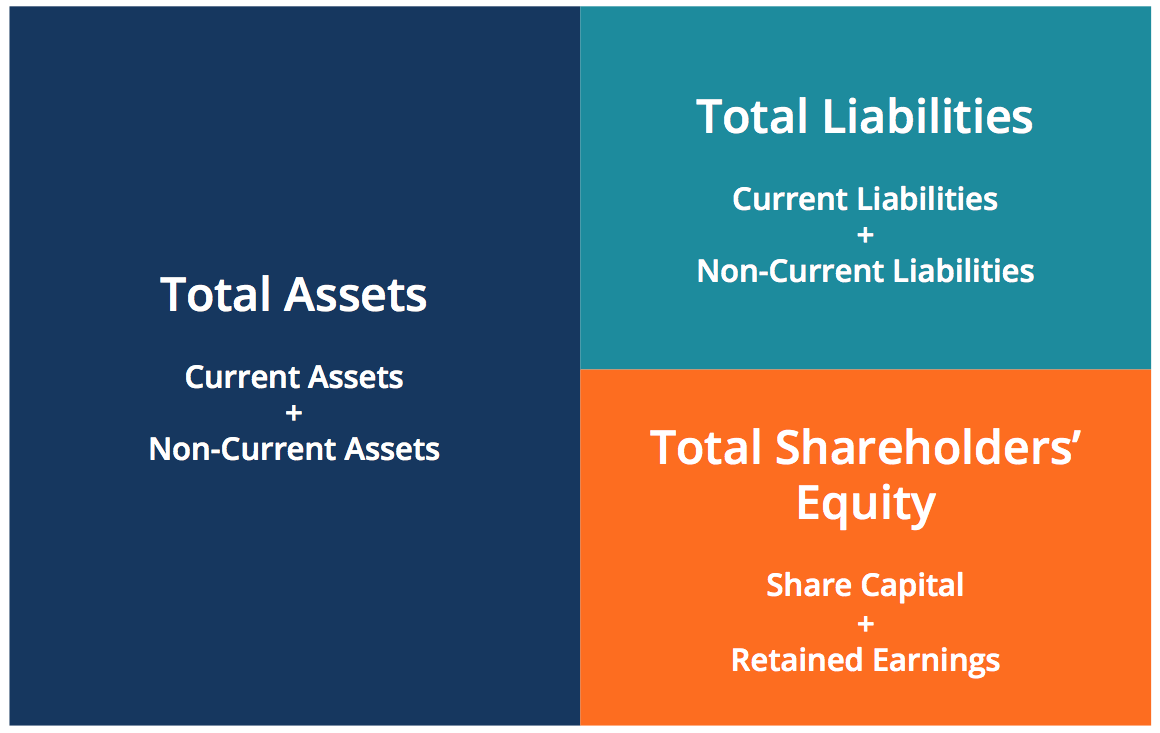
In other words, this equation allows businesses to determine revenue as well as prepare a statement of retained earnings. This then allows them to predict future profit trends and adjust business practices accordingly. Thus, the accounting equation is an essential step in determining company profitability. For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts. For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity.
- This statement reflects profits and losses that are themselves determined by the calculations that make up the basic accounting equation.
- Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
- Liabilities are amounts owed to others relating to loans, extensions of credit, and other obligations arising in the course of business.
- Profits retained in the business will increase capital and losses will decrease capital.
A company has assets totaling $50,000 and equity of $20,000. What are their liabilities?
To learn more about the balance sheet, see our Balance Sheet Outline. Drawings are amounts taken out of the business by the business owner. They will therefore result in a reduction in capital.
Income and retained earnings
(Note that, as above, the adjustment to the inventory and cost of sales figures may be made at the year-end through an adjustment to the closing stock but has been illustrated below for completeness). A liability, in its simplest terms, is an amount of money owed to another person or organization. Said a different way, liabilities are creditors’ claims on company assets because this is the amount of assets creditors would own if the company liquidated. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
Liabilities and capital were not affected in transaction #3. To learn more about the income statement, see Income Statement Outline. For more insights into the accounting equation, consider enrolling in accounting courses or reading specialized literature. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
This observation tells us that accounting statements are important in investment and credit decisions, but they are not the sole source of information for making investment and credit decisions. The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle.
For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease. Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction, the accounting system is referred to as the double-entry accounting or bookkeeping system. The accounting equation is the backbone of the accounting and reporting system.
Journal entries often use the language of debits (DR) and credits (CR). A debit refers to an increase in an asset or a decrease in a liability or shareholders’ equity. A credit in contrast refers to a decrease in an asset or an increase in a liability or shareholders’ equity. It shows that assets owned by a company are coupled with claims by creditors and lenders (liabilities), and by the owners of the business (capital). Notice that every transaction results in an equal effect to assets and liabilities plus capital.
Does the stockholders’ equity total mean the business is worth $720,000? Because many assets are not reported at current value. For example, although the land cost $125,000, Edelweiss Corporation’s balance sheet does not report its current worth. Similarly, the business may have unrecorded resources, such as a trade secret the complete guide to franchise tax or a brand name that allows it to earn extraordinary profits. Alternatively, Edelweiss may be facing business risks or pending litigation that could limit its value. Consideration should be given to these important non-financial statement valuation issues if contemplating purchasing an investment in Edelweiss stock.
It is central to understanding a key financial statement known as the balance sheet (sometimes called the statement of financial position). The following illustration for Edelweiss Corporation shows a variety of assets that are reported at a total of $895,000. Creditors are owed $175,000, leaving $720,000 of stockholders’ equity. So now we’re on the right hand side of the equation, right?
コメントを残す